Geowebinar Insights

The report examines the geological, structural, and fluid–geochemical characteristics of the Blagodatnoye gold deposit, located in the Zangarskaya part of the Yenisei Ridge and controlled by a system of deep-seated faults. The report describes the host rocks, ore body types, and mineral composition, including the distribution of native gold in quartz-vein zones and variations in gold fineness.
In the report, microthermometric studies of fluid inclusions in quartz allowed the identification of pre-ore, ore, and post-ore hydrothermal stages, with reconstructed homogenization temperatures, salinities, and pressures. The ore stage is shown to be characterized by the highest temperatures and pressures combined with moderately elevated salinity.
The report presents the results of Raman spectroscopy and gas chromatography–mass spectrometry analyses of the gas phase of fluid inclusions. Fluids dominated by CO₂ and methane were identified, and fundamental differences were revealed between volatiles released from quartz, sulfides, and native gold. Fluids associated with gold are characterized by reduced water and CO₂ contents and strong enrichment in organic compounds.
The data presented in the report indicate more reducing conditions for fluids associated with native gold compared to those related to quartz–sulfide assemblages. The potential role of organic compounds in gold transport and precipitation, including the formation of organometallic complexes, is discussed, expanding current concepts of gold deposit formation mechanisms.

The presentation examines the transformation of the global mineral exploration system and financing models over recent decades, based on the author’s international professional experience. The evolution of the roles of major mining companies, state geological surveys, and junior exploration companies within the exploration and discovery chain is analyzed.
It is shown that discovery statistics have deteriorated over time, leading to increased risks and a redistribution of functions: large companies increasingly reduce in-house exploration teams and transfer early-stage exploration to junior companies. Particular attention is paid to the late-1990s turning point, marked by stricter international reporting regulations for mineral resources and reserves and the emergence of independent competent persons.
Using examples from projects in Russia and abroad, the report discusses financial, institutional, and geopolitical constraints, as well as the characteristics of the modern venture-based junior exploration model. The conclusions emphasize the long-term nature of these trends and their implications for the future of mineral exploration and mineral resource replenishment.

The report examines a geological prospecting model for chromite mineralization in alpine-type ultramafic rocks based on the structural–lithological organization of ophiolite massifs. Alpine-type chromite ores are shown to be characterized by a limited number of industrial types, which enables the construction of generalized predictive models at regional and local scales.
Special attention is paid to the role of structural–lithological complexes of the mantle section and their zonation. The main types of complexes, their position within the section, and their relationship to ore localization are described. Typical ore-controlling structures, including pocket-like contact bends, dyke-like dunite offshoots, and zones of variable dunite thickness, are considered.
Geochemical and petrophysical prospecting criteria are analyzed. The significance of primary geochemical anomalies in nickel, iron, manganese, vanadium, and cobalt is demonstrated, along with the limitations imposed by superimposed metamorphism. The ambiguity of magnetic anomaly interpretation under serpentinization is noted, and the necessity of an integrated exploration approach is emphasized.

The report presents the results of long-term studies of hydrothermal and metasomatic processes associated with the formation of uranium deposits, with a focus on carbonate host rocks. It is shown that metasomatic alteration systematically precedes ore deposition and forms a distinct zonation of altered rocks.
Special attention is given to the role of near-ore metasomatism, its classification, and its relationship with tectonic settings. The paper summarizes concepts developed within the Russian geological school in the second half of the 20th century, including the theory of metasomatic zonality and the potential for mathematical modeling of material processes.
Case studies from specific ore fields demonstrate that dolomitization, ankeritization, silicification, and fluorite mineralization are accompanied by redistribution and enrichment of radioactive elements, primarily uranium. Detailed mapping of metasomatites is shown to significantly enhance the efficiency of exploration and improve localization of ore bodies.
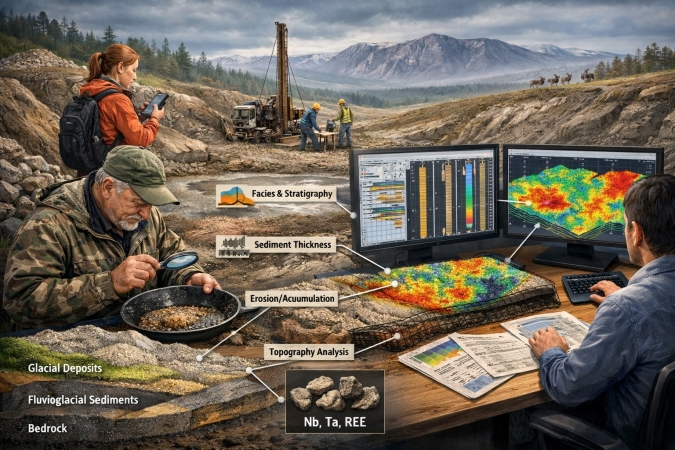

The report presents a computerized method for forecasting ore-bearing areas based on the formalization of expert geological reasoning. The approach aims to reproduce the key stages of expert decision-making and implement them as an algorithm capable of producing results comparable to those of highly experienced specialists.
The method was tested on lujavrite-related rare-metal placers located at the periphery of the Lovozero massif and associated with glacial and fluvioglacial deposits. The study area was divided into regular grid cells characterized by digital elevation model parameters, lithology, sedimentary cover thickness and ore grades. The working hypothesis assumes that expert forecasting includes factor selection, semi-quantitative evaluation and optimization of their spatial relationships.
Facies-stratigraphic, tectonic and morphometric factors were identified, normalized and analyzed for correlation with mineralization. A multiplicative index was used to integrate these factors, providing stable and contrasted predictive patterns. Comparison with exploration data demonstrates the practical applicability of the method for targeting further geological exploration.
The approach was also applied to forecasting primary mineralization and compared with machine learning results, showing similar efficiency. The method is considered a promising tool for reducing uncertainty in mineral exploration.
The report examines methodological approaches to lithochemical surveys based on mechanical dispersion flows in open territories with a dense river network. Existing sampling methods used in regional geochemical surveys are analyzed, and their limitations related to ignoring differences in dispersion processes in streams of different orders are demonstrated. Particular attention is paid to the loss of correlation between element contents in higher-order stream alluvium and primary bedrock sources of mineralization.
The report shows that a stable correlation between primary and secondary geochemical halos is characteristic mainly of first-order streams, weakens in second-order streams, and is practically absent in third-order streams. This significantly limits the reliability of ore system geometry, formation type assessment, and resource forecasting when traditional sampling schemes are applied. Typical geological and landscape settings leading to distorted geochemical signals are considered, including weakly dissected tundra areas, mountainous regions with wide terraces, and placer-bearing terrains.
The report substantiates the need for a modified sampling methodology focused on first-order streams and erosional gullies. The approach involves sampling bottom sediments at the mouths of first-order streams with drainage areas of 2–8 km² and forming composite samples from spatially close points. This methodology reduces geochemically uncharacterized areas, preserves the relative additivity of element contents, and improves the comparability of anomalies from ore bodies of different scales.
The proposed methodology described in the report provides a more uniform distribution of observation points and enables the delineation of geochemical halos that objectively reflect element distribution in bedrock. Despite a lower sampling density compared to standard schemes, the method increases data informativeness and facilitates the transition from semi-quantitative to quantitative geochemical analysis. Results of regional testing confirm its effectiveness in identifying ore objects and prospective complex anomalies at early exploration stages.
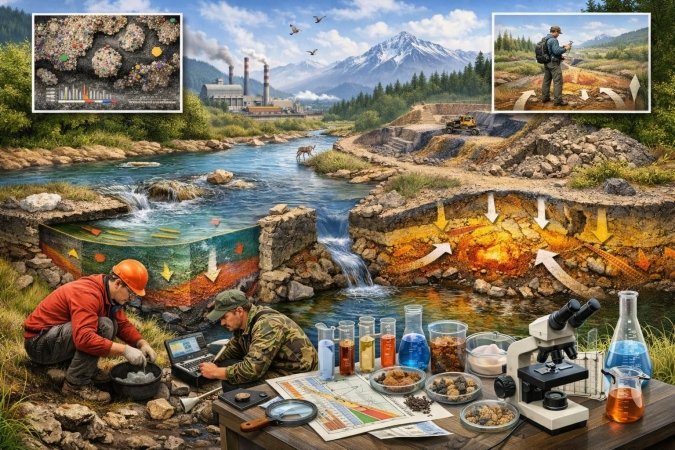

The report examines the potential for joint use of geochemical survey data from stream sediments and dispersion halos in mineral exploration and geoenvironmental studies. It is shown that geochemical anomalies formed in fluvial deposits and dispersion zones reflect both ore potential and the current state of the natural environment. The features of stream and halo anomaly formation, their relation to lithofacies conditions, hydrodynamic regimes, and geochemical settings are analyzed. The role of sediment grain-size composition and secondary redistribution processes in data interpretation is emphasized. An integrated approach is substantiated, allowing increased efficiency of geochemical surveys, refinement of ore potential assessments, and simultaneous evaluation of anthropogenic impacts on the geological environment.
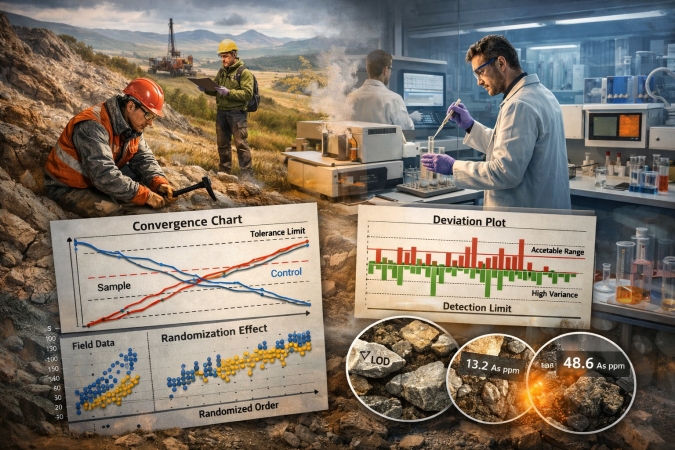

The report addresses methodological and metrological aspects of geochemical data quality control in exploration and regional surveys. The limitations of traditional approaches based on guidelines from the 1960s–1980s are analyzed in the context of modern data volumes and analytical techniques.
Special attention is given to distinguishing random uncertainty from systematic error. It is shown that systematic effects may arise from human and instrumental factors as well as from natural heterogeneity of the geochemical environment. Randomization of analytical sequences is discussed as an effective tool for breaking correlations between sampling order and laboratory analysis time.
Graphical quality control methods, including convergence and relative deviation plots, are considered, with emphasis on data behavior near detection limits and the effects of analytical quantization. The applicability limits of standard laboratory accuracy criteria to geochemical datasets are critically assessed.
The report substantiates the use of relative, standardized indicators at early stages of interpretation and proposes an integrated QA/QC and data quality improvement approach tailored to exploration geochemistry.

The report examines the application of factor analysis for processing large geochemical datasets in the construction of predictive geochemical maps. It is demonstrated that statistical methods significantly reduce data volume by replacing dozens of single-element maps with a limited number of factor maps reflecting common element accumulation processes.
The study is based on geochemical sampling of bottom sediments from the O-41 million-scale map sheet covering the Middle Urals within the Eastern Ural megazone. A brief geological and structural overview of the area is provided, including lithology, magmatism, and tectonic framework.
The data processing workflow is described, including selection of informative elements, elimination of low-variance and extreme values, and subsequent factor analysis. Five factors were identified and interpreted as copper-pyrite, iron-manganese, silver-tin, uranium-thorium, and chromium-nickel-cobalt associations.
The results show that zones of high factor values generally correlate well with the distribution of key elements and with known ore mineralization types. One factor is linked to gold-silver deposits hosted in volcanic rocks. The study confirms the high predictive efficiency and reliability of factor analysis in regional geochemical interpretation.

The report examines the potential of using biotite composition as an indicator of magmatic fertility and porphyry mineralization potential, based on the Shakhtaminsky intrusive complex in Eastern Transbaikalia. The study focuses on the Shakhtaminsky molybdenum-porphyry and Bystrinsky copper-porphyry deposits associated with multiphase Late Jurassic intrusions. Porphyry mineralization is shown to be related only to a limited number of late-phase intrusive bodies emplaced within a narrow time interval.
Biotite, as a stable mineral sensitive to melt composition and fluid conditions, was analyzed by electron microprobe methods. Previously proposed fertility criteria were tested, and a discriminant statistical analysis was performed. Biotite from ore-bearing stocks is characterized by elevated MgO contents, low capture coefficients indicating enrichment of F and Cl in the fluid phase, and compositions close to the hematite–magnetite buffer, reflecting high oxygen fugacity.
Commonly used biotite discrimination diagrams were found to be of limited applicability due to strong overlap between ore-bearing and barren fields. A new discrimination diagram based on statistical analysis is proposed, highlighting F, CO₂, Mg, and TiO₂ as key parameters. Testing of the diagram demonstrates high classification accuracy for copper-porphyry systems and moderate accuracy for molybdenum-porphyry systems, suggesting that biotite composition can be an effective tool for identifying fertile porphyry-related magmatic systems, subject to further validation.

The report discusses the use of standard borehole geophysical logging methods for identifying intervals potentially associated with polymetallic mineralization. Although logging is widely applied for technological control and lithological subdivision, its predictive potential for ore mineralization remains underutilized.
By correlating gamma logging, gamma-gamma logging, and resistivity logging data with core descriptions and geochemical analyses, a typological classification of logging curves was performed. Informative classes corresponding to elevated element contents were identified and interpreted as geophysical criteria for ore prediction.
The study demonstrates that background shifts related to variations in host-rock composition significantly affect logging parameters. To overcome this limitation, double-difference parameters were introduced, enabling classification in conditional levels and reducing dependence on absolute values.
A micro-scale zoning approach, analogous to surface geophysical zoning, allowed the identification of combined anomalies interpreted as prospective intervals. Testing on an independent site confirmed the correspondence between predicted zones and elevated element concentrations, supporting the applicability of semi-automatic classification for prioritizing sampling intervals.
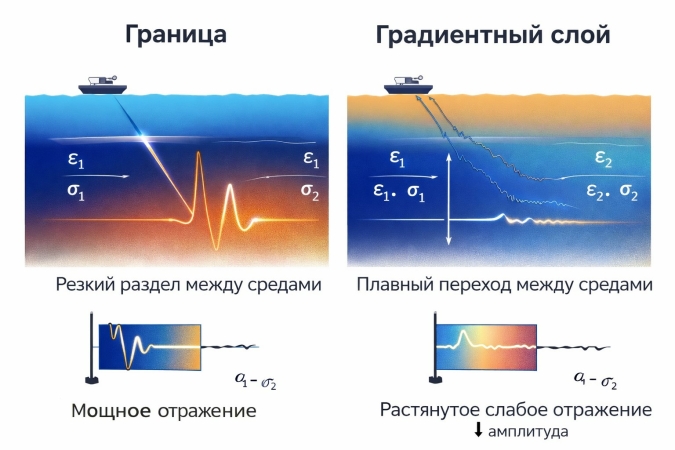
The report presents the results of ground-penetrating radar (GPR) investigations aimed at studying water-column stratification and mixing processes of waters with different temperature and salinity in lakes, river mouths, and coastal marine environments. It is shown that GPR is capable of detecting not only sharp interfaces but also extended gradient layers associated with thermoclines and gradual changes in mineralization, which generate stable radar reflections.
Field observations demonstrate that reflecting horizons within the water column are highly dynamic and may exhibit quasi-periodic oscillations interpreted as internal waves. Spectral analysis of time-expanded radargrams reveals characteristic periods of these oscillations. Comparison of GPR data with temperature, salinity, and optical measurements confirms the physical origin of the observed reflections and their relation to variations in dielectric permittivity.
Numerical modeling using the GPRMax package was performed to interpret the observed effects. The gradient layer was approximated by a sequence of thin sublayers with smoothly varying dielectric permittivity. The modeling shows that, under certain conditions, a single reflected pulse is formed, similar in shape to a reflection from a sharp boundary but shifted in time. These results were independently confirmed by controlled laboratory experiments with a stable temperature gradient.
The study emphasizes the importance of clearly distinguishing between a “boundary” and a “gradient layer” in the interpretation of GPR data in conductive media. The different roles of dielectric permittivity and electrical conductivity at early and late recording times are discussed. The results significantly expand the potential applications of GPR in hydrology, hydrogeology, and studies of natural water mixing processes.

The report addresses modern tectonophysical approaches to seismic hazard assessment of active faults in Central Asia, with the Tien Shan region taken as a key example. Special attention is paid to the analysis of recent strong earthquakes, including events with magnitudes around 7, and their relationship to the stress state of the Earth’s crust. The region is shown to be highly seismic, with indications of a possible termination of a long-term period of relative seismic quiescence.
The core of the report focuses on methods for reconstructing regional stress fields and evaluating the hazard of individual fault segments. Algorithms for determining the orientation of principal stress axes, calculating normal and shear stresses on fault planes, and applying Mohr diagrams to identify zones close to brittle failure are described. These approaches form the basis for ranking active faults according to their potential seismic hazard.
Preliminary maps of hazardous fault segments are presented for the North-Central Tien Shan, Altai, Baikal region, and Eastern Anatolia. The importance of dedicated web-based resources providing access to lithospheric stress data and information on active faults across Eurasia is emphasized.
A separate discussion is devoted to the ambiguity in selecting the actual rupture plane when interpreting earthquake focal mechanisms from seismological data. The need for rejecting unreliable solutions and applying independent kinematic and tectonophysical verification methods is highlighted.
The report concludes with prospects for long-term and intermediate-term earthquake forecasting, including the use of satellite interferometry, GNSS observations, seismic noise analysis, and borehole monitoring. Particular emphasis is placed on the practical importance of estimating potential hypocenter depths for assessing seismic hazard levels.

The report examines the possibility of combining structural–geomorphological analysis with a tectonic fragmentation assessment method to identify active fault zones in the upper lithosphere. The study is carried out for the Greater Caucasus and Sakhalin Island, regions characterized by different geodynamic settings.
Digital elevation models, seismic catalogs, and databases of active faults are used as primary data. Structural–geomorphological analysis makes it possible to delineate weakened zones interpreted as potential locations of active faulting. These zones are further applied as input data for calculating a tectonic fragmentation coefficient based on the density and total length of lineaments within defined spatial cells.
The resulting maps and profiles of tectonic fragmentation show a high degree of correspondence with known active faults and seismicity patterns. For Sakhalin Island, a clear tendency of earthquake epicenters to concentrate within areas of high tectonic fragmentation is revealed, whereas for the Greater Caucasus this relationship is less pronounced. Overall, the proposed approach demonstrates its effectiveness for mapping recent fault structures and assessing zones of potential shallow seismic activity.

The report addresses the problem of identifying and mapping cryogenic landforms under conditions of intensified thermodenudational processes associated with contemporary climate warming. It is shown that permafrost degradation is reflected in the spectral characteristics of the Earth’s surface and can be detected using remote sensing data combined with modern cloud-based data processing technologies.
The aim of the study was to compare supervised classification methods based on machine-learning algorithms for GIS mapping of cryogenic relief on Orga Island. Sentinel satellite imagery supplemented with spectral indices and principal component analysis was used to create a multi-band composite dataset.
Several generalized land-surface classes representing different degrees of thermodenudational activity were identified, followed by semi-automated mapping and accuracy assessment. The results demonstrate that different machine-learning algorithms exhibit varying performance for specific classes, supporting a differentiated approach to algorithm selection in cryogenic geomorphological studies.

